Methods of Powering of Drones
Drones have revolutionized several industries with their unique aerial technology. The drones are powered by various methods of power, most of them being battery power.
Not every drone is powered by a battery. One needs to know the various methods of powering drones in order to identify a suitable drone for the purpose.
Overview of Drone Technology
Drone technology also has a variety of applications, ranging from recreational to commercial applications like aerial photography, agriculture, and search and rescue. Power source of a drone are also determinants of their performance by flying time, carrying capacity, and the ability to use.
Battery-Powered Drones
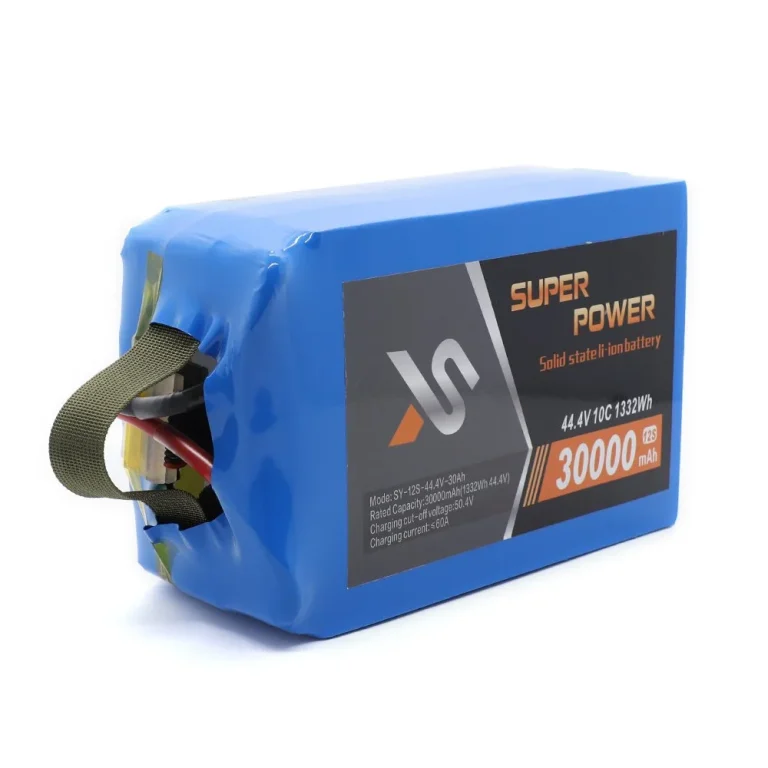
Battery-powered drones are the mass market’s preference due to convenience and ease of operation. Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries and Li-po batteries with high energy density and acceptable cycle life are the first preference to drive such drones.
Features of Battery-Powered Drones
Lithium-ion batteries are particularly used for drone batteries based on their distinguished characteristics.
Taixing Shengya Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., for instance, uses its SY-7S-25.55V-31Ah model to deliver a super high energy density of 270wh/kg to 340wh/kg for efficient power supply.
Flight Time
Capacity and drone capacity determine battery-powered drone flight time. Battery-powered drones can have a flight time of 20 to 30 minutes using two battery recharge cycles.
Portability
Battery-powered drones are highly portable because they are light and compact. Portability makes it possible for them to be used in the field where deployment should be rapid.
Advantages
Cost-Effective
Battery-powered drones are also highly affordable in comparison with others. They are low-maintenance or no-maintenance and also cost-effective to operate as they do not use fuel or have complex systems.
Eco-Friendly
Battery-powered drones release no gases when operating, and thus, they do not cause any form of harm to the environment. They also release no noise while in flight, thus preventing noise pollution.
Versatility
The ease of battery-powered drones sees them utilized across different environments and uses, from recreational photography to business surveying.
Limitations
Despite a few advantages of battery-powered drones, they have some limitations that must be highlighted by the user.
Short Flight Time
The most limiting factor is reduced flight duration due to restrictions on the batteries. The user would need additional batteries or be stuck having to continually recharge them should there be increased usage.
Batteries Lose Their Strength
Lithium-ion batteries depreciate and lose their functionality through a number of charges and discharge cycles over a period. This reduces the functionality of the drone and comprises repetitive battery changes.
Weather Sensitivity
Battery life can be lost due to bad or hot weather, taking into account the drone’s strength in bad weather.
Non-Battery-Powered Drones
Though battery power is prevalent, there are other sources of power utilized in some applications in drones.
Fuel-Powered Drones
Fuel-based drones running on gasoline or diesel are fueled by engines with the aim of achieving longer flight times and higher payloads. They are employed in heavy-duty activities but with a higher requirement for maintenance as well as environmental damage in the way of emissions.
Solar-Powered Drones
Solar panels installed on the drone allow solar drones to harness the energy of the sun for utilization in providing longer flight times. Drones are optimally suited for long-term surveillance but are still hampered by the daylight hours and weather.
Tethered Drones
Tethered drones operate continuously through a wire connected to an inlet inserted into the ground station and thus stay airborne for extended hours as and when needed. Tethered drones are also designed primarily for communication or recon missions but still enjoy freedom of movement through the tethering system.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Drones
Hydrogen fuel cells are a renewable energy source with longer flight duration than standard batteries. Hydrogen production and storage require sophisticated infrastructure.
Wind-Powered Drones
Wind-powered drones operate on wind turbines or sails. They are in experimental stages but show some potential in sustainability and longer flight time for environments with higher wind speeds.
Battery-Powered Drones vs. Non-Battery-Powered Drones
When choosing between battery-powered drones and non-battery-powered drones, several factors come into play. Both of them have advantages and disadvantages, which are appropriate for certain uses and client requirements.
Flight Time and Endurance
Battery-powered drones also will be able to fly for 20 to 30 minutes after being charged, depending on battery capacity and the model of drone. Compared to non-battery-powered drones such as fuel or tethered drones, there are more flying times because they employ other power sources.
Payload Capacity
Payload capacity is also something that must be taken into account. Battery-powered drones are less ideal for heavy use, although they provide greater payload capacity than fuel-powered drones, which are, however, ideal for heavy use. Lithium-ion battery technology used in the SY-7S-25.55V-31Ah model, for example, is rapidly closing this gap with greater energy density and improved power delivery.
Environmental Impact
Battery-powered drones are also commonly known as being green because they emit nothing when flying. They are therefore a green and environmentally friendly alternative to fuel-based drones that emit greenhouse gases. Solar drones also offer a green alternative using the sun to energize flight for a longer period but without the ability to control the weather.
Cost and Maintenance
Battery-powered drones are more cost-effective with minimal maintenance cost and zero maintenance requirements. Gas drones have maintenance costs on an engine from time to time with additional fuel cost. Tethered drones could be costly with installation cost only at the onset since it is a patented product.
Choosing the Best Drone for Your Application
Choosing the right drone is based on a checklist of factors based on your needs and constraints.
Application
Look at the main use of the drone. If indoor or toy use, then a battery-powered drone is enough with its lightness and easy maneuverability. For commercial use where payload and time are an issue, then non-battery types can be utilized.
Budget
Your budget will also determine the type of drone you will be in a position to afford. Battery-powered drones offer inexpensive options with little operating cost relative to other systems like hydrogen fuel cell or solar power drones.
Environment
The circumstances under which you will be flying also need to be considered. If you are flying under extreme weather or temperature conditions, hot or cold, then the effect that this will have on battery life or the energy input to solar panels needs to be considered.
Flight Duration and Payload Requirements
Compare your flight time needs with the application. For long flight times with no stopgap recharging or refueling break, use non-battery solutions such as tethered systems or fuel-based systems.
Taixing Shengya Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., established in 2017 in Jiangsu Province, this firm aims to be the world’s first battery company in high energy density lithium-ion batteries, overall enhancing drone performance in any use. For any user looking for reliable drone batteries to satisfy their needs-from extended flight time with high-energy density batteries like SY-12S-43.2V-35Ah to the guarantee of stable power supply through the likes of SY-7S-25.55V-31Ah.